Finding the area of a square might seem as simple as pie—if pie were a perfectly shaped piece of geometry. But don’t let its straightforwardness fool you. Understanding how to calculate the area opens doors to a world of math magic, from home improvement projects to artful design.
Imagine impressing friends with your newfound knowledge of squares while casually discussing how to tile a floor or design a garden. It’s not just about numbers; it’s about wielding the power of math like a superhero. So, grab your calculator and a pencil, and let’s dive into the delightful world of squares, where every side is equal, and the area is just a formula away.
Table of Contents
ToggleUnderstanding the Concept of Area
Understanding area involves recognizing how much space an object occupies. A square’s area reflects its expanse within two dimensions.
Definition of Area
Area defines the amount of surface within a shape’s boundaries. For regular shapes, such as squares, one can calculate area using straightforward formulas. The area of a square equals the length of one side multiplied by itself, or side squared. This simplicity makes it accessible, aiding in quick calculations when determining sizes or spaces.
Importance of Area in Geometry
Area plays a critical role in geometry. It serves as a foundation for understanding shapes and their properties. Calculating area is crucial for real-world applications, including architecture and land measurement. Professionals rely on this knowledge for accurate design and planning. Utilizing area calculations improves efficiency in material usage and overall space management. Understanding area also enhances problem-solving skills necessary for advanced geometric concepts.
The Formula for Area of a Square
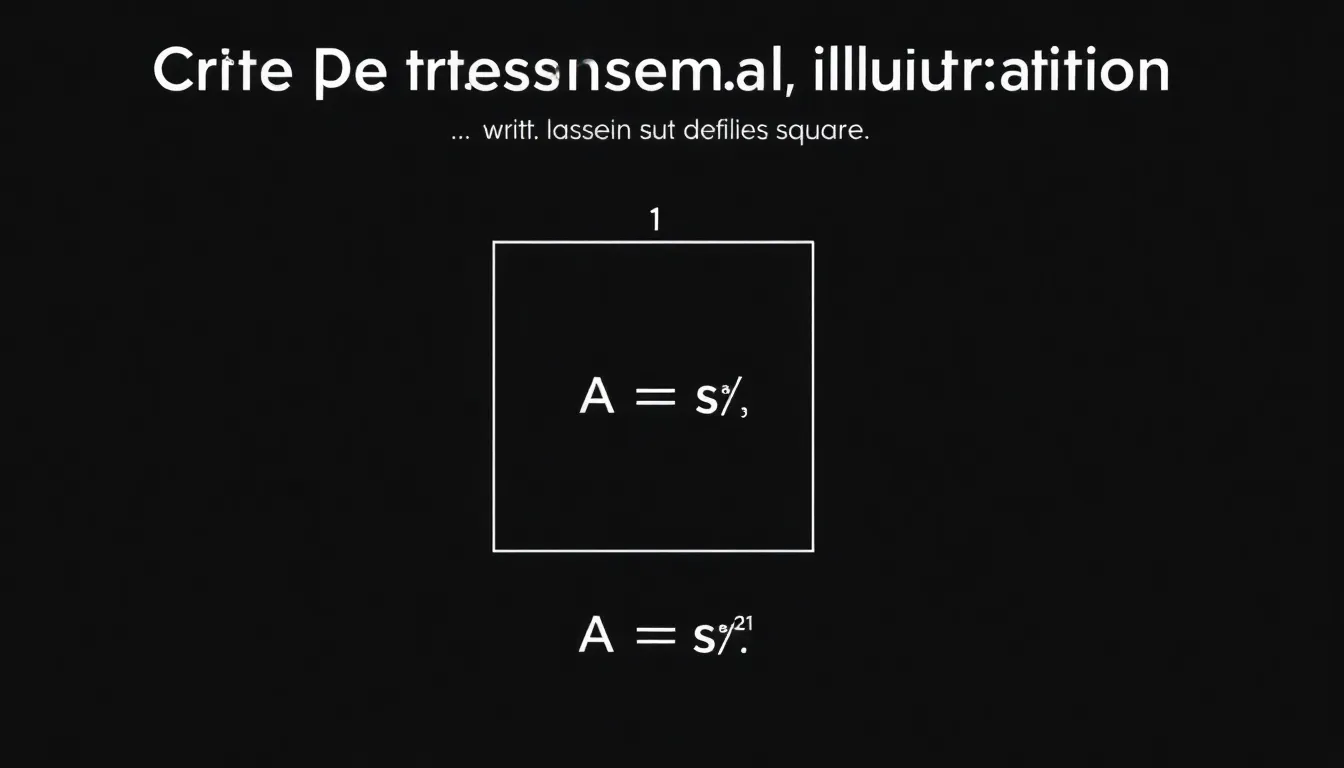
Calculating the area of a square relies on a straightforward formula. The relationship between the side length and the area simplifies this distance into a manageable calculation.
Deriving the Formula
To derive the formula for a square’s area, consider a square with equal side lengths, denoted as ( s ). By multiplying the length of one side by itself, the formula becomes ( A = s times s ). This expression can be shortened to ( A = s^2 ). Each side’s uniform length emphasizes the property of squares, ensuring the area remains consistent across all dimensions. Every square offers an opportunity to see how area functions in geometric applications.
Components of the Formula
The formula consists of key components that contribute to calculating a square’s area. The variable ( s ) represents the length of one side. By squaring this value, it gives the total number of unit squares that fit within the larger square’s limits. Knowing the side length directly impacts the area measurement. For instance, a square with a side length of 4 units has an area of ( 4^2 = 16 ) square units. Each side length measurement corresponds precisely to the area found within the shape’s borders.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Find Area of Square
Finding the area of a square involves straightforward steps. Understanding each step ensures accurate calculations.
Measuring the Sides
Start by determining the length of one side of the square. Using a ruler or measuring tape provides precise measurements in units like inches or centimeters. It helps if the square sits flat for easier measurement. Taking care to measure only one side suffices, as all sides are equal in length. For instance, if one side measures 5 units, every side will also measure 5 units. Record this measurement clearly for reference.
Applying the Formula
Upon measuring the side, apply the area formula A = s². Replacing the variable s with the measured length makes the formula simple to use. Squaring the length represents multiplying the side by itself. For example, with a side length of 5 units, the calculation becomes 5 × 5. This results in an area of 25 square units. Such a systematic approach ensures accurate and efficient area calculations for any square encountered.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Understanding how to find the area of a square involves avoiding common pitfalls. Mistakes in measurement and formula application often lead to incorrect results.
Incorrect Measurements
Accurate measurements serve as the foundation for calculating area. Using a ruler or measuring tape with precision ensures correct dimensions. Rounding numbers or reading the scale incorrectly can cause errors. For example, measuring one side as 4.5 units when it is actually 4.7 units leads to an inaccurate area calculation. Always double-check measurements to confirm consistency across all sides, as even minor discrepancies can yield significant differences in the final area.
Misapplication of the Formula
Misapplying the area formula for a square can skew results. The formula A = s² requires squaring the side length. Failing to square the value, such as simply using the side length, results in an incorrect area measurement. For instance, using a side length of 6 units directly as the area calculates to 6 instead of the correct area of 36 square units. Following the formula precisely is crucial for obtaining accurate and meaningful area calculations.
Understanding how to find the area of a square is essential for various practical applications. This knowledge not only aids in everyday tasks but also builds a foundation for more complex mathematical concepts. By mastering the formula A = s² and following accurate measurement techniques, anyone can confidently tackle area calculations. Avoiding common mistakes ensures precise results, making it easier to apply this skill in real-life scenarios. Embracing the simplicity and significance of calculating area opens doors to improved problem-solving and effective space management.







